Preparing the Server to Use for User Authentication
When using Windows authentication or LDAP authentication as the user authentication method for the first time, check that your server environment meets the requirements for user authentication, and configure the required settings.
To use Windows authentication
Prepare the server as follows:
Check the requirements of Windows authentication.
Install the Web server (IIS) and the Active Directory Certificate Service in the server.
Create a server certificate.
You do not need to create a server certificate to transmit user information that is not encrypted.
To use LDAP authentication
Check the requirements of LDAP authentication, and configure the settings according to the server environment as necessary.
Requirements of Server Authentication Used for User Authentication
Items | Explanation |
|---|---|
Usable OS | Windows Server 2008/2008 R2/2012/2012 R2/2016/2019
|
Authentication method | Supports the following authentication methods:
To specify Kerberos authentication, the server authenticating users must support Kerberos authentication. If the server does not support it, NTLM authentication is automatically selected. |
Requirements for authentication |
|

The server can authenticate users managed in other domains, but cannot obtain information such as an e-mail address.
When Kerberos authentication is enabled, the e-mail address cannot be obtained if SSL/TLS is specified.
Even if you edit an authenticated user's information, such as an e-mail address, in the machine's Address Book, it may be overwritten by the information from the server when authentication is performed.
If you created a new user in the domain controller and selected "User must change password at next logon" at password configuration, first log on the computer and change the password.
If the Guest account on the Windows server is enabled, users not registered in the domain controller can be authenticated. When this account is enabled, users are registered in the Address Book and can use the functions available under [*Default Group].
Items | Explanations |
|---|---|
Usable version | LDAP Version 2.0/3.0 |
Authentication method |
When you select Cleartext authentication, LDAP simplified authentication is enabled. Simplified authentication can be performed with a user attribute (such as cn or uid) instead of the DN. |
Requirements for authentication |
|
Notes when the LDAP server is configured using Active Directory
When Kerberos authentication is enabled together with SSL/TLS, the e-mail address cannot be obtained.
Anonymous authentication might be available. To improve security, set anonymous authentication to Disable.

Even if you edit an authenticated user's information, such as an e-mail address, in the machine's Address Book, it may be overwritten by the information from the server when authentication is performed.
Under LDAP authentication, you cannot specify access limits for groups registered in the server.
Do not use double-byte Japanese, Traditional Chinese, Simplified Chinese, or Hangul characters when entering the login user name or password. If you use double-byte characters, you cannot authenticate using Web Image Monitor.
When using the machine for the first time, the user can use Available Functions specified in [User Authentication Management].
To specify Available Functions for each user, register the user together with Available Functions in the Address Book, or specify Available Functions in the user registered automatically in the Address Book.
Installing the Web Server (IIS) and the "Active Directory Certificate Service"
Install the required service in the Windows server to obtain user information registered in Active Directory automatically.
Windows Server 2012/2016/2019
 On the [Start] menu, click [Server Manager].
On the [Start] menu, click [Server Manager].
 On the [Manage] menu, click [Add Roles and Features].
On the [Manage] menu, click [Add Roles and Features].
 Click [Next].
Click [Next].
 Select [Role-based or feature-based installation], and then click [Next].
Select [Role-based or feature-based installation], and then click [Next].
 Select a server, and then click [Next].
Select a server, and then click [Next].
 Select the [Active Directory Certificate Service] and [Web Server (IIS)] check boxes, and then click [Next].
Select the [Active Directory Certificate Service] and [Web Server (IIS)] check boxes, and then click [Next].
If a confirmation message appears, click [Add Features].
 Check the features to install, and then click [Next].
Check the features to install, and then click [Next].
 Read the content information, then click [Next].
Read the content information, then click [Next].
 Make sure that [Certification Authority] is selected in the Role Services area in Active Directory Certificate Services, and then click [Next].
Make sure that [Certification Authority] is selected in the Role Services area in Active Directory Certificate Services, and then click [Next].
 Read the content information, then click [Next].
Read the content information, then click [Next].
When using Windows Server 2016, proceed to Step 12 after reading the content information.
 Check the role services to install under Web server (IIS), and then click [Next].
Check the role services to install under Web server (IIS), and then click [Next].
 Click [Install].
Click [Install].
 After completing the installation, click the notification icon of the server manager, and then click [Configure Active Directory Certificate Service on the destination server].
After completing the installation, click the notification icon of the server manager, and then click [Configure Active Directory Certificate Service on the destination server].
 Click [Next].
Click [Next].
 Check [Certification Authority] in the role service, and then click [Next].
Check [Certification Authority] in the role service, and then click [Next].
 Select [Enterprise CA], and then click [Next].
Select [Enterprise CA], and then click [Next].
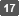 Select [Root CA], and then click [Next].
Select [Root CA], and then click [Next].
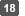 Select [Create a new private key], and then click [Next].
Select [Create a new private key], and then click [Next].
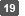 Select a cryptographic provider, key length, and hash algorithm to create a new private key, and then click [Next].
Select a cryptographic provider, key length, and hash algorithm to create a new private key, and then click [Next].
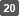 In [Common name for this CA:], enter the Certificate Authority name, and then click [Next].
In [Common name for this CA:], enter the Certificate Authority name, and then click [Next].
 Select the validity period, and then click [Next].
Select the validity period, and then click [Next].
 Leave [Certificate database location:] and [Certificate database log location:] without change, and then click [Next].
Leave [Certificate database location:] and [Certificate database log location:] without change, and then click [Next].
 Click [Configure].
Click [Configure].
 When the message "Configuration succeeded" appears, click [Close].
When the message "Configuration succeeded" appears, click [Close].
Windows Server 2008 R2
 On the [Start] menu, point to [Administrative Tools], and then start the server manager.
On the [Start] menu, point to [Administrative Tools], and then start the server manager.
 Click [Roles] in the left column, click [Add Roles] from the [Action] menu.
Click [Roles] in the left column, click [Add Roles] from the [Action] menu.
 Click [Next].
Click [Next].
 Select the [Web Server (IIS)] and [Active Directory Certificate Services] check boxes, and then click [Next].
Select the [Web Server (IIS)] and [Active Directory Certificate Services] check boxes, and then click [Next].
If a confirmation message appears, click [Add Features].
 Read the content information, and then click [Next].
Read the content information, and then click [Next].
 Check [Certification Authority], and then click [Next].
Check [Certification Authority], and then click [Next].
 Select [Enterprise], and then click [Next].
Select [Enterprise], and then click [Next].
 Select [Root CA], and then click [Next].
Select [Root CA], and then click [Next].
 Select [Create a new private key], and then click [Next].
Select [Create a new private key], and then click [Next].
 Select a cryptographic service provider, key length, and hash algorithm to create a new private key, and then click [Next].
Select a cryptographic service provider, key length, and hash algorithm to create a new private key, and then click [Next].
 In [Common name for this CA:], enter the Certificate Authority name, and then click [Next].
In [Common name for this CA:], enter the Certificate Authority name, and then click [Next].
 Select the validity period, and then click [Next].
Select the validity period, and then click [Next].
 Leave [Certificate database location:] and [Certificate database log location:] without changing, and then click [Next].
Leave [Certificate database location:] and [Certificate database log location:] without changing, and then click [Next].
 Read the notes, and then click [Next].
Read the notes, and then click [Next].
 Select the role services to install, and then click [Next].
Select the role services to install, and then click [Next].
 Click [Install].
Click [Install].
Installation of added features starts.
Creating a Server Certificate
To encrypt user information, create a server certificate in the Windows server. Windows Server 2016 is used as an example.
 On the [Start] menu, point to [All Applications], and then click [Internet Information Service (IIS) Manager] of [Administrative Tools].
On the [Start] menu, point to [All Applications], and then click [Internet Information Service (IIS) Manager] of [Administrative Tools].
 In the left column, click [Server Name], and then double-click [Server Certificate].
In the left column, click [Server Name], and then double-click [Server Certificate].
 In the right column, click [Create Certificate Request...].
In the right column, click [Create Certificate Request...].
 Enter all the information, and click [Next].
Enter all the information, and click [Next].
 In [Cryptographic service provider:], select a provider, and then click [Next].
In [Cryptographic service provider:], select a provider, and then click [Next].
 Click [...], and then specify a file name for the certificate request.
Click [...], and then specify a file name for the certificate request.
 Specify a location in which to store the file, and then click [Open].
Specify a location in which to store the file, and then click [Open].
 Click [Finish].
Click [Finish].
