The AC transfer technology is used for the belt-to-paper transfer, to support printing on textured media.
Negatively charged toner image (-) on the ITB [6] is transferred to the paper by applying a negative bias (-) to the paper transfer bias roller [7].
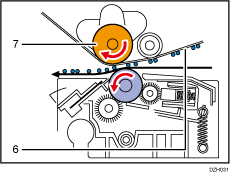
Following are the two types of negative bias applied to the paper transfer bias roller:
DC bias: For all media types
AC bias: When 1218: [Paper Transfer Output: Textured Paper Mode] is enabled
Bias is adjustable by print mode because the optimum bias level is dependent on the amount of toner transfer.
(Bias is higher for FC than for BW/Special due to the greater amount of transferred toner.)
The illustration below describes how AC transfer transfers toner to textured media.
By nature of AC, in which the current flows in an alternating up-and-down movement, toner particles sync with this movement. Toner transferred to the media is pulled back to the ITB to gain further transferability, enabling toner particles to fall into the indentations on the rough surfaced media.
Textured paper mode
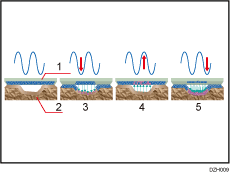
ITB
Textured paper
Toner is partially transferred.
Toner transferred to the paper returns to the belt and combines with toner remaining on the belt.
Toner is transferred to the indentations on the surface of the paper.

AC transfer inactive
AC transfer active
Bias correction can be adjusted for each imaging mode, because the optimum bias correction value varies depending on the transferred toner. (More bias correction is required for printing in FC/FCS mode, which consumes more toner than printing in BW/S mode.)
Related Advanced Settings
DC bias
AC bias