The IP-Fax function sends or receives documents between two facsimiles directly via a TCP/IP network.
Overview of functions
This function has the following advantages and is suitable for communication within the same LAN:
Reducing communication costs
Communicating between IP-Faxes at higher speed than by standard fax
IP-Fax uses SIP and H.323 as the network protocol.
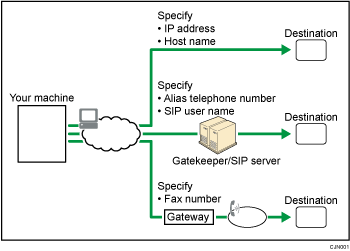
IP-Fax destinations
Specify an IP address or host name instead of a fax number.
Example of an IP address: 192.168.1.10
Example of a host name: IPFAX1
When using a gatekeeper, specify an alias telephone number.
Example of an alias telephone number: 0311119999
When using a SIP server, you can send by specifying SIP user name.
Example of a SIP user name: ABC
You can also transmit to a G3 facsimile connected to the public switched telephone network (PSTN) via a gateway (T.38-compliant).
Example of a fax number: 03-1234-5678
You can receive IP-Faxes in the same manner as standard faxes. For details about reception, see Types of Reception.
![]() (mainly Europe and Asia)
(mainly Europe and Asia)
For details about the optional units required for this function, see "Functions Requiring Optional Configurations", Getting Started.
![]()
IP-Fax supported by this machine is ITU-T Recommendation T.38 compliant.
SIP allows you to transmit and receive documents over an IPv6 network.