Sending to Folder Destinations (Folder Destinations)
You can specify a folder destination by selecting a Destination key from the destination list.
![]()
To send to a folder destination, you must first register the path for the folder in the Address Book. You cannot enter the path on the standby display. For details about how to register a folder destination, see “Registering Addresses and Users for Facsimile/Scanner Functions”, Network and System Settings Reference.
![]() Press [Folder] to switch the transmission type to folder.
Press [Folder] to switch the transmission type to folder.
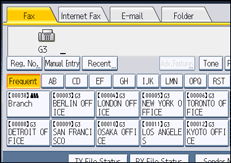
![]() To set the file type, press [File Type].
To set the file type, press [File Type].
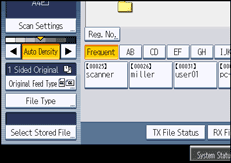
Select [TIFF] or [PDF], and then press [OK].
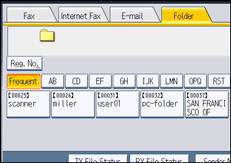
![]() Press the Destination key to specify a destination.
Press the Destination key to specify a destination.
![]() Specify the next destination.
Specify the next destination.
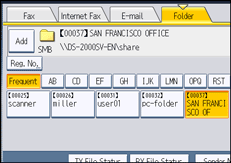
To add another folder destination, press the next Destination key.
Press the transmission type tab to switch the transmission type between fax/IP-Fax, Internet Fax, e-mail, and folder.
![]() Press the [Start] key.
Press the [Start] key.
The machine starts to scan the original and stores it in memory. When scanning ends, the Communicating indicator lights and transmission starts.
![]()
Folder transmission is performed using Memory Transmission, which automatically starts transmission after storing documents in memory. If you switch the type of transmission to folder while the machine is in Immediate Transmission mode, the transmission mode is automatically switched to Memory Transmission.
For details about canceling a transmission, see “Canceling a Transmission”.
The Facsimile Features menu includes a user parameter setting (switch 17, bit 2) that enables you to configure the machine to force the user to press [Add] whenever s/he specifies a destination using a destination key. This prevents users accidentally sending documents to the wrong destination. See “Parameter Settings”.
For details about a folder destination, see “Folder Transmission”.