Bypassing the SMTP server
You can send e-mail documents directly to their destinations without going through the SMTP server.
Normally, e-mail is sent through the SMTP server. With this feature however, the domain part of the destination's e-mail address is read as the SMTP server's address and transmissions bypass the SMTP server. Since this reduces the load on the server, you can send e-mails without having to take into account the transfer time from server to destination.
![]()
To use this function, the following settings must be specified:
In “System Settings”, “SMTP Server”, in “File Transfer”, set the port number to “25”.
To specify the host name of the other party as the domain part of the e-mail address, register the host name of the other party on the DNS server.
For details about these settings, see “System Settings”, “Special Operations under Windows”, Network and System Settings Guide.
If the other party's IP address is not registered on the DNS server, specify the IP address at the domain part of the e-mail address.
To send a document over an IPv6 network, you must specify the other party's host name (not IP address) as the domain part.
To use this function, the other party's computer or server must:
be in an environment where e-mail can be received
be connected to the same LAN as this machine
support SMTP reception and have its reception protocol set to SMTP
SMTP authentication set on the other party's computer or server is disabled when e-mail is sent using this function.
If e-mail is sent from the other party using this function, even if reception fails, Error Mail Notification is not sent to the sender.
When e-mail is sent using this function, even if transmission fails, the server does not send error notification e-mail.
When using this function, you cannot send e-mail to the administrator e-mail address that is registered on this machine.
There are two ways of specifying a destination, as follows:
By specifying the other party's host name
Specify a destination's e-mail address by adding the other party's host name to the domain part of the e-mail address. Specify the address after the @ as follows: “host name”, “. (dot)”, and “domain name”.
xxxx@host name of the other party.domain name
For example, if the other party's e-mail address is “abc@defcompany.com” and the host name is “HOST”:
abc@HOST.defcompany.com
By specifying the other party's IP address
Specify a destination's e-mail address by changing the domain part of the e-mail address to the other party's IP address.
xxxx@[the other party's IP address]
For example, if the other party's e-mail address is “abc@defcompany.com” and the IP address is “192.168.1.10”:
abc@[192.168.1.10]
Use the following procedure to bypass the SMTP server.
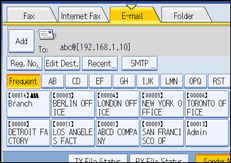
![]() Press [SMTP].
Press [SMTP].
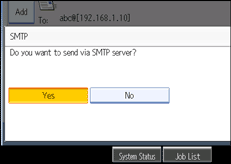
![]() Press [No].
Press [No].
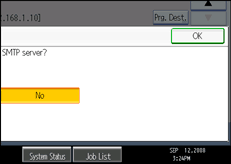
![]() Press [OK].
Press [OK].
![]()
If you use [Manual Entry] to specify the destinations directly, you can also specify whether or not to use SMTP server for each destination.
If you use the destination list to select the destinations, the SMTP server setting specified in the Address Book is enabled.